Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment in Koramangala, Bangalore
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory disorder. This means it is a condition whereby your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the healthy tissues through the release of inflammatory chemicals.
What do we need to know about Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis can occur in any part of the body but more commonly affects wrist joints, hands, knees, hips and other parts of the body such as skin, eye, heart and blood vessels.
Treatment options for Rheumatoid Arthritis usually include pain relief medications, occupational therapy and surgery. Orthopaedic hospitals in Bangalore offer impressive care and treatment for all types of rheumatoid arthritis.
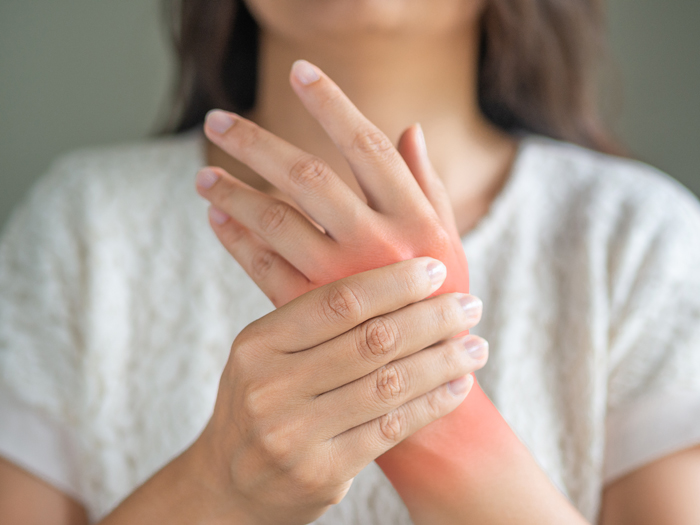
What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Symptoms usually vary from person to person. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Stiffness and swelling of joints
- Joint pain
- Fatigue
- Tenderness and weakness of joints
- Fever
- Inflammation
What are the causes and risk factors of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The specific cause of rheumatoid arthritis is yet to be known. The following are some of the risk factors that are believed to increase a person's risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis:
- Genetics and heredity
- Age
- Infectious diseases
- Gender - women are more prone to develop RA than men
- Hormones
- Smoking
- Physiological factors like stress
- Obesity
To seek treatment, you can visit orthopaedic hospitals in Koramangala as well.
When do you need to consult a doctor for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Early prognosis and treatment of RA can significantly reduce the risks and delay the progress of the disease.
If you`re experiencing any potential signs and symptoms or if you are facing any difficulties in your normal activities, it is always better to seek immediate medical assistance for guidance and treatment.
You can request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Koramangala, Bangalore.
Call 1860 500 2244 to book an appointment.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis treated?
There is no cure for RA, but treatment can help patients lead a normal life. Depending on the complexity and severity of the disease condition, your doctor may advise the following treatments.
- Topical and OTC medications: The following are some of the commonly prescribed medications to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are used to treat mild and early-stage cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis to eliminate pain caused by inflammation. Most common NSAIDs include OTC medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen and other similar pain relief medications.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs restrain the body`s autoimmune response and helps in slowing the progress of the disease. Few examples include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine.
- Biologic response modifiers: Also known as biologic agents, these are a newer class of medication that blocks specific parts of immune response rather than blocking the entire body`s immune response. Few examples include abatacept and baricitinib.
- Topical medication: It is available in various forms such as cream, spray and gel, and can be easily administered on the surface of the inflammation site to help you get rid of the pain. Some examples include diclofenac sodium gel and topical capsaicin.
- Occupational therapy: Physiotherapy and occupation therapy may help patients to cope with the chronic pain caused by inflammation. Moderate exercises and massages on the affected region can improve your mobility and speed up muscle recovery.
- Surgery: Surgical options to treat Rheumatoid Arthritis are considered as the final option of treatment. Some of the most common surgical procedures are as follows,
- Joint replacement surgery - this involves replacing the damaged joints by synthetic joints. Some of the common types of joint replacement surgery include:
- Total hip replacement surgery
- Total knee replacement surgery
- Shoulder replacement surgery
- Synovectomy - this involves surgical removal of affected synovial tissues around the joint to relieve the symptoms.
Conclusion
Although Rheumatoid Arthritis remains an incurable autoimmune disorder, early detection and treatment can help patients to cope with the condition. Fortunately, with the right kind of treatment and lifestyle changes, most patients can lead a normal life
Some of the common diagnostic methods include:
- General physical examination
- Review and analyses of medical history
- Blood test. The following blood tests may help your doctor to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis:
- Evaluated levels of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Higher levels of antinuclear antibodies in the blood
- Imaging tests: X-ray, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan
Although you cannot completely prevent the disease, some of the following lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the symptoms:
- Adopting healthier eating habits
- Limited exposure to environmental pollutants
- Losing weight
RA flare refers to sudden worsening or increase in symptoms of the disease. RA flare can cause intense pain and last for several days or several months.
Symptoms
Treatments
Our Top Specialities
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








