Meniscus Repair Treatment in Koramangala, Bangalore
Meniscal tear is quite a common knee wound. A forceful spin or twist of the knee can damage the meniscus tissue. A torn meniscus leads to ache, soreness and stiffness. This can limit the knee's rotation movement and cause difficulty in extending the leg fully.
Orthopedic specialists suggest treatment for a torn meniscus based on the type, size, and location of the tear. You can check for the best orthopedic surgeon in Koramangla. Or you can search online for an orthopedic specialist near me.
What is meniscus repair?
The meniscus refers to two C-shaped discs of cartilage located at the outer edge of the knee joint and inside the knee. It cushions and connects the femur to the tibia, i.e. thigh bone and shinbone. It facilitates knee movement by stabilizing the joint, acting as a shock absorber, distributing body weight evenly, providing lubrication and supporting balance by sending signals to the brain.
Conservative methods to relieve pain and promote self-healing of a meniscal tear include resting, applying ice packs, compression, elevation and medications. Your doctor might also recommend physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and in the legs to help secure and stabilize the knee joint.
These treatments are not an efficient option for an acute meniscal tear though. Complex tears that are large, unstable or cause locking symptoms require surgery to repair and heal the meniscus tear.
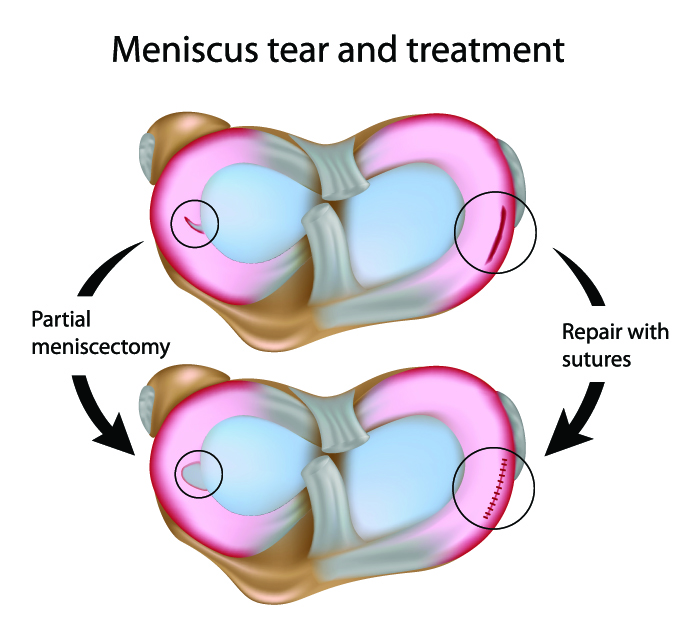
Meniscectomy is a type of surgery recommended by orthopedic specialists to treat a severely damaged meniscus.
Who qualifies for meniscus repair?
You have to meet certain factors to qualify for a meniscus repair such as:
- You are healthy and want to continue living an active lifestyle
- You understand and accept the rehabilitation process and duration
- You accept the risks of surgery
- The tear is situated in the margin of the meniscus
Why is meniscus repair conducted?
Appropriate meniscus repair is suggested depending on the pattern, location or severity of the tear. If your symptoms persist after three months or increase, your doctor may recommend surgery.
When do you need to see a doctor?
Surgery is required when:
- Conservative treatment such as icing or rest wasn’t effective in healing the tear
- Alignment of the knee joint is shifted
- Knee gets locked while doing routine activities
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Koramangla, Bangalore
Call 1860 500 2244 to book an appointment
What are the different types of surgery? What is the basic procedure?
Your doctor might suggest any of the following: meniscus repair, partial meniscectomy or total meniscectomy.
Arthroscopic surgery is an outpatient procedure. It is the preferred choice of surgery as it causes less muscle and tissue damage and facilitates faster recovery. The doctor will make a few small cuts in your knee. He/she will then insert an arthroscope, a thin flexible tube with tools and a camera attached to it. The tear is repaired using the tools, and this is known as meniscus repair. Meniscectomy is an arthroscopic procedure in which the damaged meniscus is partially or totally removed. Lastly, the incision is closed with a suture or surgical tape strips. The surgery takes about an hour.
What are the benefits of meniscus repair?
A successful meniscus repair helps conserve meniscus tissue and restore the knee’s functionality. Other benefits of meniscus repair include:
- Enhanced mobility
- Improved knee stability
- Less pain
What are the risks?
Generally, meniscectomies are safe surgical procedures but there are risks such as:
- Infection: If the wound is not cleaned and dressed regularly, it can increase the risk of infection. Consult a doctor if you notice signs of discomfort, soreness or drainage from the surgical site. You will be prescribed antibodies to prevent the spread of infection.
- Deep venous thrombosis: After surgery, leg movements are restricted to regain strength, which reduces blood flow and increases the risk of clots. You will be prescribed blood thinners or compression stockings to help prevent blood clots. Keep your knee and leg elevated to prevent this from occurring.
Furthermore, a total meniscectomy can increase your risk of developing osteoarthritis in your knee. Therefore, partial meniscectomy is a preferred option with a better long-term outcome.
Conclusion
Recovery time is usually about four to six weeks, depending on several factors such as the surgical approach used, the severity of the injury, daily activity level, overall health, and response to physical therapy. Reach out to an arthroscopy surgeon in Koramangla to discuss the different meniscus repair options and select the treatment that suits you the best.
A physical examination can help detect a meniscus tear. Your doctor might rotate your knee and leg into different positions, observe your walk and ask you to squat to evaluate the symptoms. You might also be recommended imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI to determine the kind of injury and discuss appropriate treatment options.
Sports players are more prone to sudden meniscus injuries. Also, certain forms of exercises such as kneeling, squatting or lifting heavy weights can increase the risk of meniscus tears. Older people are at potential risk of meniscus damage due to degeneration of bones and tissues from wear and tear.
Meniscus repair surgery using arthroscopy is a minimally invasive and safer treatment option. However, surgery can cause some complications such as swelling, infection, knee stiffness, skin nerve injury and blood clots. These can be treated with medication and physiotherapy.
Symptoms
Our Top Specialities
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








