Management of Open Fracture Treatment in Kondapur, Hyderabad
Open fractures are mainly caused because of road accidents. With the improvement of the traffic rules and safety equipment in motor vehicles, road accidents have reduced significantly. This resulted in a decrease in the open fractures cases. Cyclists, motorcyclists, and pedestrians are the ones who are prone to road accidents and have open fractures.
Handling open fractures is very complicated. This is because there are complex bone fractures and tissue damages. The loss of blood is also a concern.
In the last few years, the management of open fracture has improved drastically with the introduction of algorithms and the integration of orthoplastic management in Apollo Kondapur.
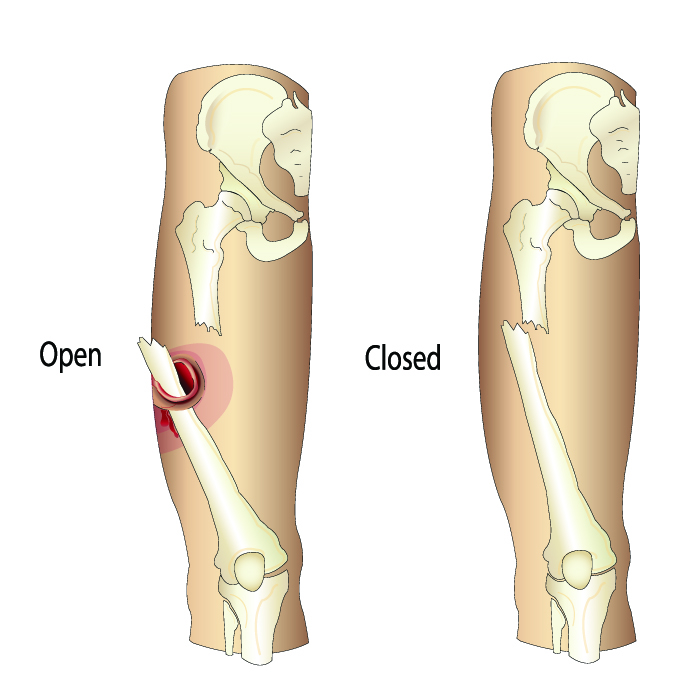
What are the Types of Open Fractures?
Fractures are classified into grades. They are:
Grade 1: Grade 1 fractures are simple fractures that are caused by low-energy traumas. The damage causes low contamination and good soft tissue coverage. The wound size is less than 1cm.
Grade 2: Grade 2 fractures are caused by moderate trauma, in grade 2 fractures there is more soft tissue damage and the wound size is more than 1cm. The fracture patterns are more complex.
Grade 3: The grade 3 fractures are caused by high-energy trauma. Usually, the size of the wound is greater than 10cm. The damage on the soft tissue is extensive and the contamination is high. The fracture pattern is severe and needs immediate medical attention. The grade 3 fractures are sub-classified into three grades depending on the extent of the injuries. They are grade 3A, grade 3B, and grade 3C.
What is the Initial Management of the Open Fractures?
To approach the open fracture we must be aware of the following managements:
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis: This process involves the administration of antibiotics before contamination. This is done by performing surgical incisions and this is given to prevent infections at the open fracture. Antibiotic prophylaxis must be given as early as possible because it reduces the chance of infection.
- Time of Debridement: In the early days the time of debridement used to be 6-hours. This means that the fractured area should be cleaned of any debris in the first 6 hours. This is done to prevent infections, but there is enough evidence to prove that the infections rate does not depend on the time of debridement. This debridement can be done in the first 24 hours for the best state of the fractured area.
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy: Negative pressure wound therapy is done on fractures or wounds that cannot be closed. In this therapy, the negative pressure is disturbed and evenly distributed across the wound. The risk of infection and other complications are involved.
- Compartment Syndrome: This occurs in cases of high-energy traumas and non-conscious patients. The compartment pressure should always be measured beforehand for such cases. If the pressure increases then fasciotomy has to be performed.
- Initial Fixation: This is done for open fractures. The femur and tibia are the most common areas. To reduce the pain and improve the wound proper fixation must be obtained.
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Kondapur
Call 1860-500-2244 to book an appointment
What are the Complications?
Complications depend on the type of fracture or grade of the fracture.
For Grade 1 fractures the chances of complications are very low and if treated properly the patient will recover very fast.
For Grade 2 fractures the chances of complications will be a little high. Infections can occur at the site and delay recovery.
For Grade 3 fractures the chances of complications are very high and the wounded area can cause blood loss and form infections. The recovery will take months to heal. Immediate medical attention is required in such cases.
Management of open fractures is the guide to how to handle open fracture wounds and take proper steps for the best results. It’s like protocols for the surgery of open fractures that must be implemented by the doctors.
Depending on the grade of the fracture it can take from 6-8 weeks for small grade 1 and 2 injuries. For severe cases, it can take about 20 weeks.
- Try to stop the bleeding by applying pressure.
- Use a clean sterile cloth for the bandage.
- Apply ice packs to the affected area this will reduce pain and swelling.
Symptoms
Our Top Specialities
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








