Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment in Chirag Enclave, Delhi
One of the biggest complications of diabetes is diabetic retinopathy. This affects the eyes by damaging the blood vessels in the retina.
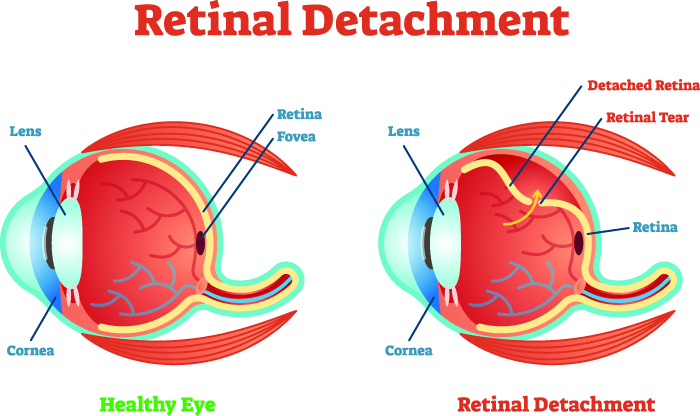
The retina is the light-sensitive tissue or screen that forms the image of any object we see. Diabetic retinopathy may initially cause no symptoms or only minor visual disturbances, but it may cause blindness in the long term.
If you have been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy recently, you just need to search for a specialist in ophthalmology near me or an ophthalmology hospital near me or a diabetic retinopathy hospital near me.
What are the major types?
There are mainly two types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Early diabetic retinopathy
- Advanced diabetic retinopathy
What are the symptoms?
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, there might be no symptoms at all. You may experience the following with the progression of the disease:
- Blurring of vision
- Floating black spots or thin lines (floats) in the field of vision
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Fluctuating vision
- Vision loss
What causes diabetic retinopathy?
Over time, high blood sugar can block the small blood vessels that supply the retina, cutting off the supply. New blood vessels grow in response that do not develop normally and leak easily.
When do you need to see a doctor?
Treatment of diabetes at the right time is the best preventive measure for loss of eyesight. It is always a good idea for diabetics to get thorough eye examinations on an annual basis. Pregnancy also adds to the chances of developing diabetic retinopathy.
If you are pregnant, your ophthalmologist may recommend additional eye exams during pregnancy. If your vision suddenly changes or becomes blurred, consult an ophthalmologist immediately.
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Chirag Enclave, New Delhi.
Call 1860 500 2244 to book an appointment.
What are the risk factors?
If you are diabetic, you are at risk. The following need to be monitored:
- Prolonged diabetes
- Tobacco use
- High cholesterol levels
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Hypertension
How is it treated?
Treatment largely depends on the type of diabetic retinopathy and its severity and is designed to slow or stop the progression.
- Early-stage: You may not need immediate treatment if you have mild to moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. However, close monitoring of the eye condition is recommended by most ophthalmologists. This is to make sure that you get treatment as soon as your eyes need them. Your endocrinologist will guide you further, you just follow the instructions. Blood sugar control can usually slow its progression in the early stage.
- Advanced-stage: In case you have proliferative diabetic retinopathy or macular edema, you must receive treatment immediately. Depending on your specific retinal problem, the following options are available:
- Injection of the drug into the eye
- Panretinal photocoagulation
- Photocoagulation
- Vitrectomy
Request an appointment at Apollo Spectra Hospitals, Chirag Enclave, New Delhi.
Call 1860 500 2244 to book an appointment.
Conclusion
Sadly, there is no cure for the disease. But, treatment can surely slow or stop the progression. Not to mention, diabetes is a lifelong condition that usually cannot be reversed. This makes it obvious that once diabetic, the risk of retinal damage and vision loss remains lifelong.
If you have undergone treatment for diabetic retinopathy, make sure that you do not miss your regular eye exams.
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371611
Anyone with type 1 (congenital) or type 2 (adult-onset) diabetes can develop this disease. The longer you have diabetes and the less controlled your blood sugar levels are, the more likely it is to develop this ocular complication.
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), also known as early diabetic retinopathy. It is a more common type. In this case, the new blood vessels do not grow or the vessel cells stop proliferating.
It is also known as the advanced form of diabetic retinopathy. It is a more serious type. In this case, damaged blood vessels close, causing new abnormal blood vessels to grow in the retina. The newly formed vessels break easily and affect the retina. A transparent jelly-like substance called the vitreous humor fills the center of the eyeball.
Symptoms
Our Top Specialities
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








