Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention
March 6, 2020
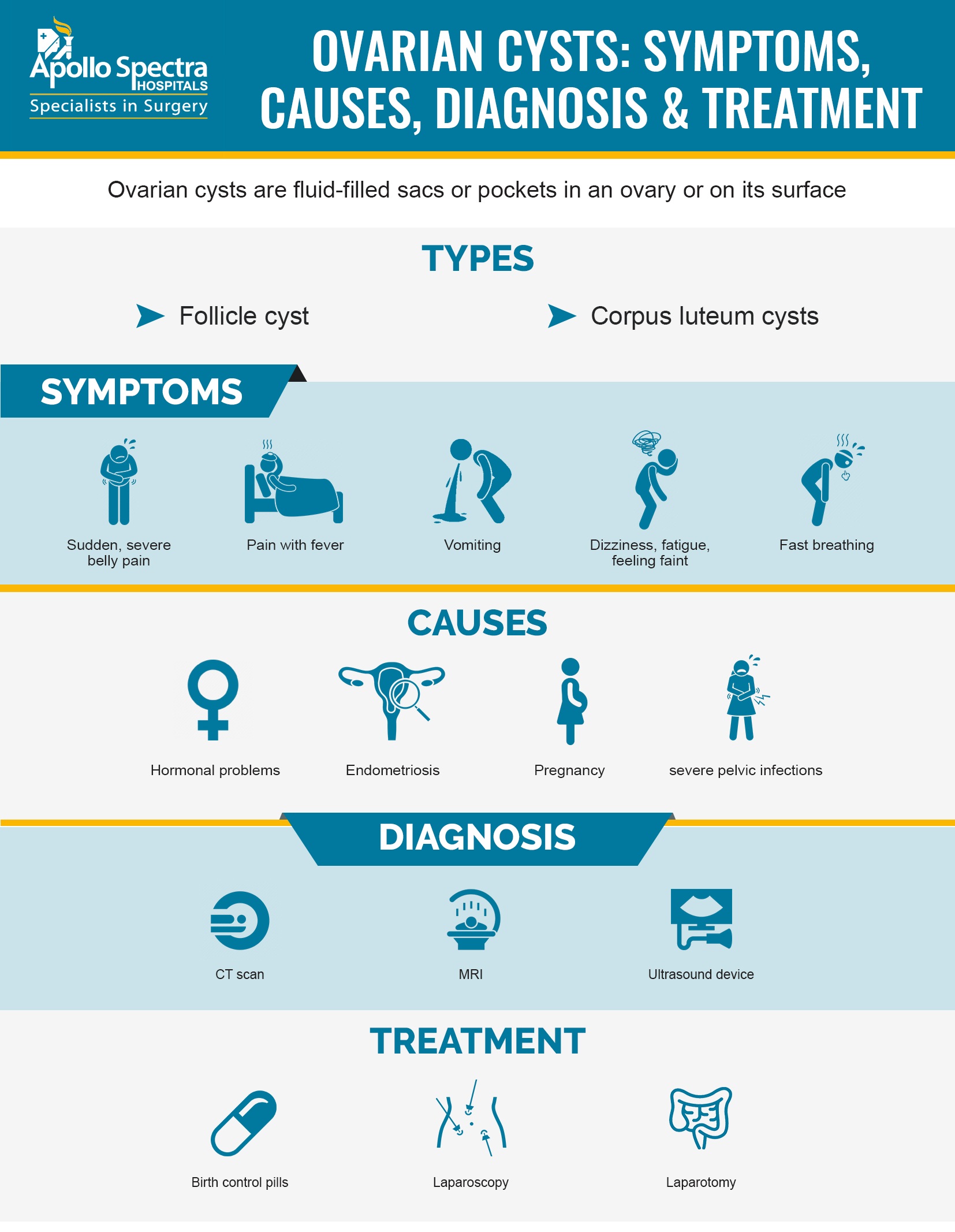
Ovarian cysts are pockets or sacs filled with fluid in an ovary or on its surface. Human females are born with two ovaries on either side of the uterus. Each of them is about the same size and shape of an almond. The ovaries develop and mature the eggs that are released in monthly cycles. Usually, ovarian cysts cause little to no issues and many women have these at some point in their life. Majority of them disappear within a few months without any treatment. However, if they get ruptured, it can lead to serious symptoms. So, to protect your health, you must be aware of the symptoms and get regular pelvic exams.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are several types of ovarian cysts and most of these are not cancerous:
- Follicular cysts - This is caused by the follicle growth. When the growth of follicle is larger than normal and does not open for releasing the egg, it results in the formation of follicular cyst. It is usually harmless and disappears within 2 to 3 menstrual cycles.
- Corpus luteum cyst - When the egg is released from the follicle, it starts producing progesterone and estrogen for conception. This follicle is now termed as corpus luteum. Sometimes, the fluid gets accumulated inside the follicle which turns the corpus luteum into a cyst.
- Dermoid cysts - Also known as teratomas, these contain tissues like skin, hair or teeth as they are created from embryonic cells. They are usually non cancerous.
- Endometriomas - This form of cyst is developed because of a condition called endometriosis. In this, the uterine endometrial cells start growing outside the uterus. Some of the tissues get attached to the ovary and start forming a growth.
- Cystadenomas - These cysts are developed on the ovary’s surface and might be filled with mucous or watery material.
Symptoms
Usually, cysts go away on their own and don’t cause any symptoms. However, if you have a large ovarian cyst, you might have the following:
- Bloating
- Heaviness or fullness in the abdomen
- A dull or sharp pelvic pain caused in on the side of the cyst in the lower abdomen
If you have sudden, severe pelvic or abdominal pain, or pain with vomiting and fever, you need to visit your doctor immediately. Also, call your doctor right away if you have rapid breathing, weakness, lightheadedness, or cold and clammy skin.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent ovarian cysts. However, you can detect them early through routine gynecologic examinations. Also, if you have the following signs, you should alert your doctor:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Changes in the menstrual cycle
- Abdominal fullness
- Loss of appetite
- Ongoing pelvic pain
Diagnosis
A pelvic exam can be used for diagnosing an ovarian cyst. However, for determining the type and whether you have to get treatment or not, the doctor might recommend some test. This will depend on the size of the cyst and whether it is solid, fluid-filled or mixed. Here are some possible diagnostic tests:
- Pregnancy test
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Laparoscopy
- CA 125 blood test
Treatment
The doctor will recommend a treatment for you on the basis of your age, your symptoms, and the size and type of the cysts. The following treatment options are available for ovarian cyst:
- Waiting - In most cases, the doctor will just recommend waiting and then re-examining to check as most of the cysts go away on their own. This option can be used for women of any age. It is preferred when you are not showing any symptoms and the diagnostic exam showed a small and simple fluid-filled cyst. However, you might have to get follow-up pelvic ultrasound a few times for making sure that the cyst is not changing in size.
- Medication - Some hormonal contraceptives might be prescribed to you. This includes birth control pills so that the ovarian cysts do not occur again. However, these pills won’t do anything for shrinking existing cysts.
- Surgery - If your cyst is large, is growing, causing pain, continues for more than 3 menstrual cycles, and doesn’t look like a functional cyst, the doctor might recommend removing the cyst surgically. One surgical option is ovarian cystectomy where the cyst is removed without the removal of the ovary. In some cases, the doctor might remove the affected ovary and leave the other just as it is. This procedure is called oophorectomy.
If a cyst is cancerous, your doctor might refer you to a gynecologic cancer specialist. You might have to undergo radiation or chemotherapy and get your ovaries, fallopian tubes, and ovaries removed through a total hysterectomy.
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








