Can an Ovarian Cyst Be Normal
June 10, 2022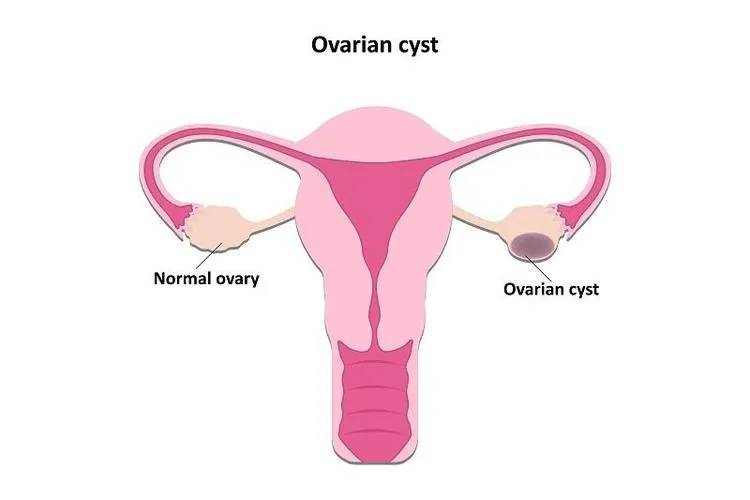
What Is an Ovarian Cyst?
An ovarian cyst is usually a pocket of fluid located within or on the surface of the ovary. Most ovarian cysts are harmless, causing little or no symptoms, and tend to disappear without treatment after a couple of months.
Ovarian cysts can be 2 to 5 cm long. Thus, depending on the type of ovarian cyst in an individual, it may be considered normal or benign or the type that requires medical and surgical intervention. All ovarian cysts are not cancerous.
How Is an Ovarian Cyst Diagnosed?
Gynaecologists can diagnose ovarian cysts, usually, by a pelvic ultrasound. It determines if there is a cyst, where it is located, and whether it is solid, fluid-filled or mixed.
What are the various kinds of ovarian cysts and their symptoms and probable lines of treatment?
- Functional Ovarian Cysts: These develop during a woman's reproductive years. They usually disappear on their own after four to eight weeks.
- Rupturing Cysts: These kinds of ovarian cysts rarely present symptoms. Pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen are symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst. It is caused by ovarian torsion, ectopic pregnancy or ovulation pain. Medical attention is needed. Typically, pain medications and observation relieve the symptoms. Surgery may be necessary to stop persistent bleeding or to stabilise blood pressure.
- Benign Neoplastic Cyst: This is a rare ovarian cyst present in various forms. An abnormal tissue growth generally characterises it. Sometimes it may cause no symptoms, but pelvic pain occurs in case of complications (cystic teratoma/dermoid cyst). Such ovarian cysts typically do not resolve on their own and need medical intervention.
- Endometriotic Cysts: Also known as "chocolate cysts", these cysts develop when endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus and gets attached to the ovaries. These generally do not dissolve and tend to rupture, causing adhesion, pelvic pain and infertility.
- Malignant/Cancerous Cysts: A malignant or cancerous cyst indicates ovarian cancer. Once diagnosed, complete removal of the cyst is necessary. An expert surgeon at a hospital with a good infrastructure should perform this.
- Ovarian Torsion: This condition occurs when ovarian cysts get enlarged to such an extent that the ovary gets twisted out of its natural position. This may partially or fully inhibit the supply of blood to the ovaries. The acute condition causes severe and sudden lower abdomen pain, nausea or vomiting. This is one of the most common gynaecological emergencies requiring immediate surgical intervention.
- Ovarian Cysts & Fertility: Typically, ovarian cysts do not interfere with fertility. An estimated 30-40% of women with endometriosis may struggle with infertility. However, some kinds of ovarian cysts may impede fertility and thus, need expert medical intervention.
What Are the Main Lines of Treatment for Ovarian Cysts?
Treatment for an ovarian cyst depends on the age of the patient, the symptoms and the type and size of the cyst. Under the able care of an expert gynaecologist, you may be treated in the following ways for an ovarian cyst:
- Sustained Treatment: This is generally done for simple, small, and fluid-filled cysts. Typically, they cause no symptoms. These are diagnosed through an ultrasound. It may require follow-up pelvic ultrasound to examine whether there is any change in the size of the cysts.
- Medication: In some cases, to keep the recurrence of ovarian cysts in check, hormonal contraceptives such as birth control pills are prescribed.
- Surgery: In cases other than functional cysts, where the size of the cysts may increase over a couple of menstrual cycles, causing lower abdominal pain, surgery may be the best option. Your gynaecologist may remove the large cyst without removing the ovary (ovarian cystectomy). The surgeon may also remove just the affected ovary (oophorectomy). Expertise is the key to this treatment.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A laparoscope helps remove an ovarian cyst in this surgical procedure. If this cyst is found to be cancerous, after a biopsy, you may be referred to a cancer specialist. This may require hysterectomy or the removal of the uterus, ovaries, and the fallopian tubes, followed by chemotherapy or radiation. An expert gynaecological oncologist team is crucial for this treatment.
- Post-Menopause Surgery: In cases where an ovarian cyst develops after menopause and causes complications, surgical intervention may be required.
In line with Apollo Spectra Hospitals' commitment to partnering with women through their healthcare journey, we provide top-of-the-line gynaecological treatments.
Backed with experienced doctors and an ever-evolving, fully equipped hospital set-up, Apollo Spectra Hospitals offers top-end gynaecological consultation, in-house diagnostics, and the latest minimally invasive surgical procedures to help patients handle ovarian cysts in a safe environment.
You may reach out to us by calling 1860-500-2244 for any ovarian cyst-related issues and treatment.
An ovarian cyst is a pocket of fluid located within or on the surface of the ovary.
An ovarian cyst can generally be diagnosed through a pelvic ultrasound.
The various kinds of ovarian cysts are Functional Ovarian Cysts, Rupturing Cysts, Benign Neoplastic Cysts, Endometriotic Cysts and Malignant/Cancerous Cysts
While some ovarian cysts may need sustained treatment, other methods include medication and laparoscopic surgery.
NOTICE BOARD
CONTACT US
CONTACT US
 Book Appointment
Book Appointment


.svg)
.svg)
.svg)
.svg)








